What You See Is What You Get:
Exploiting Visibility for 3D Object Detection
CVPR 2020
| Peiyun Hu1 | Jason Ziglar2 | David Held1 | Deva Ramanan1,2 |
|---|
2Argo AI

| Peiyun Hu1 | Jason Ziglar2 | David Held1 | Deva Ramanan1,2 |
|---|


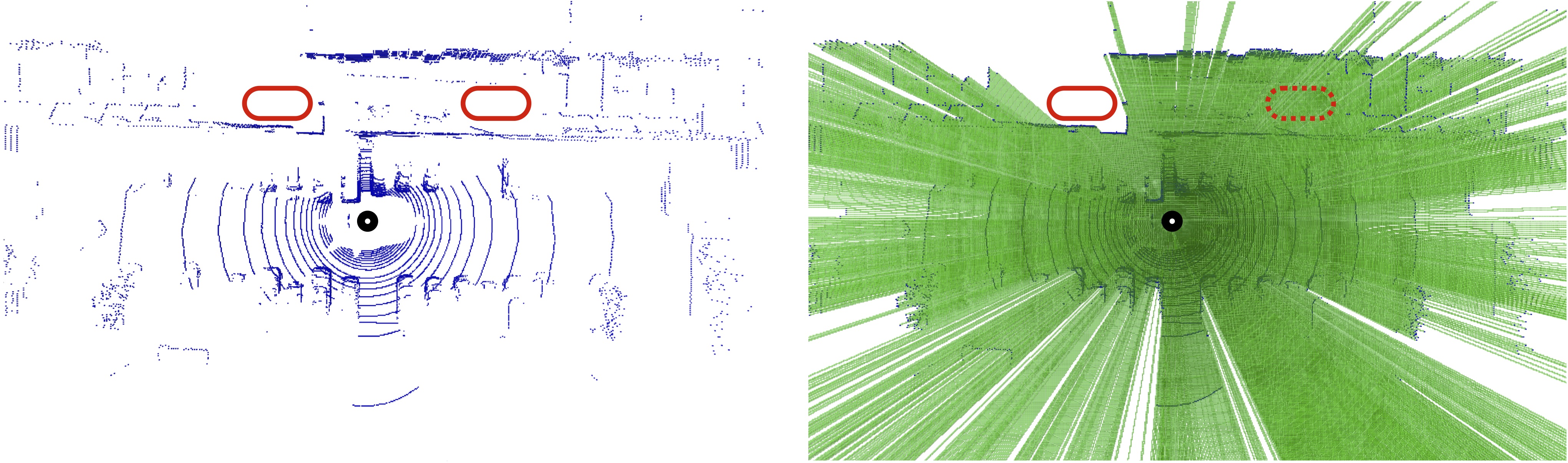
Recent advances in 3D sensing have created unique challenges for computer vision. One fundamental challenge is finding a good representation for 3D sensor data. Most popular representations (such as PointNet) are proposed in the context of processing truly 3D data (e.g. points sampled from mesh models), ignoring the fact that 3D sensored data such as a LiDAR sweep is in fact 2.5D. We argue that representing 2.5D data as collections of (x, y, z) points fundamentally destroys hidden information about freespace. In this paper, we demonstrate such knowledge can be efficiently recovered through 3D raycasting and readily incorporated into batch-based gradient learning. We describe a simple approach to augmenting voxel-based networks with visibility: we add a voxelized visibility map as an additional input stream. In addition, we show that visibility can be combined with two crucial modifications common to state-of-the-art 3D detectors: synthetic data augmentation of virtual objects and temporal aggregation of LiDAR sweeps over multiple time frames. On the NuScenes 3D detection benchmark, we show that, by adding an additional stream for visibility input, we can significantly improve the overall detection accuracy of a state-of-the-art 3D detector.
This work was supported by the CMU Argo AI Center for Autonomous Vehicle Research.